What is a Crossbite? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Have you heard of a crossbite? If not, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Many people are unfamiliar with this dental issue. A crossbite occurs when your teeth don’t align properly, potentially causing dental problems. Early treatment is important to prevent complications.
What is a Crossbite?
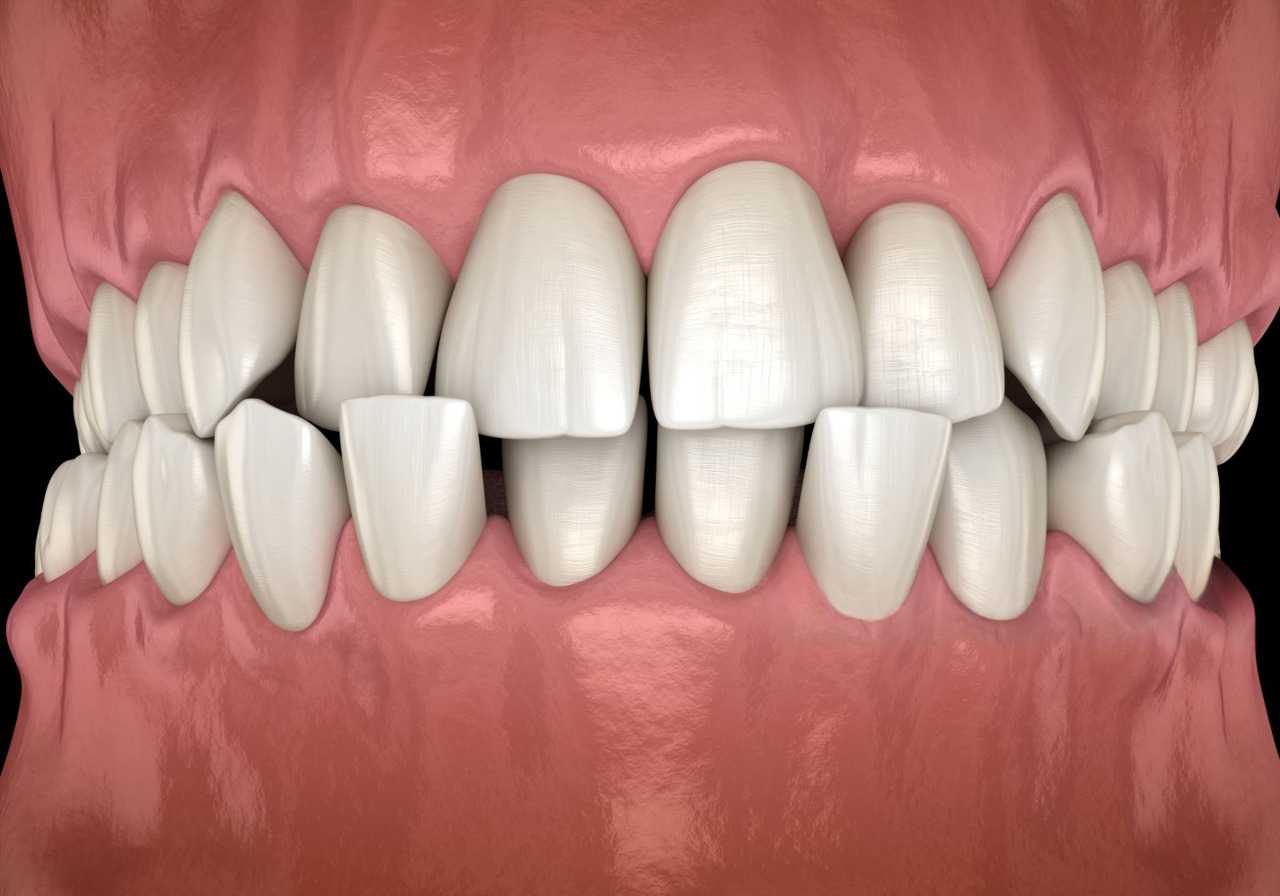 A crossbite is one common dental condition presenting when the front teeth are bent inside so as to fit only inside the opposite lower teeth with the mouth being closed. Usually, it has an effect of one or even more than that of teeth, so it may go for either side of the teeth, anterior (front), posterior (back) crossbite. If not treated, a crossbite can lead to several oral health issues that manifest in jaw pain and improper tooth wear and gum problems.
A crossbite is one common dental condition presenting when the front teeth are bent inside so as to fit only inside the opposite lower teeth with the mouth being closed. Usually, it has an effect of one or even more than that of teeth, so it may go for either side of the teeth, anterior (front), posterior (back) crossbite. If not treated, a crossbite can lead to several oral health issues that manifest in jaw pain and improper tooth wear and gum problems.
Causes of Crossbite
Several factors contribute to the development of a crossbite. Some of the common causes include:
- Genetics: If a parent or close relative has a crossbite, there are higher chances that his or her child will acquire this condition.
- Abnormal Jaw Growth: In cases where the growth rates of the upper jaw and lower jaw are different, one can end up being larger and can create a crossbite.
- Prolonged Oral Habits: Thumb sucking, extended use of pacifiers, or excessive thrusting of the tongue can all affect the way the teeth will erupt and result in a crossbite.
- Delayed Tooth Eruption: If baby teeth do not fall out on time or permanent teeth erupt abnormally, it can lead to a crossbite.
- Mouth Breathing: Children who breathe normally through their mouths rather than their noses are likely to develop malocclusion of the jaw and end up with a crossbite.
- Early Loss of Baby Teeth: Losing primary teeth too early can cause the adjacent teeth shift abnormally and cause a crossbite.
Symptoms of Crossbite
The type of crossbite may vary with its severity and the location within the mouth. Common symptoms include:
- Uneven Tooth Wear: A crossbite can lead to excessive wear affecting the teeth, causing enamel erosion and sensitivity.
- Jaw Pain and TMJ Disorders: The jaw muscles and joints are strained as a result of a crossbite. This brings about discomfort, headaches, and temporomandibular joint disorders.
- Gum Recession: In extreme cases, gum recession is caused by a crossbite as it exposes the root of the tooth, increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Difficulty Chewing or Biting: Misaligned teeth can make it hard to chew food normally, leading to digestive issues and discomfort.
- Facial Asymmetry: Prolonged misalignment can lead to uneven facial growth, especially among growing children.
- Speech Issues: Some individuals have difficulty pronouncing certain words or sounds due to improper tongue placement.
Treatment Options for Crossbite
Treatments for correcting crossbites involve various options that depend on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient. The sooner intervention is done, the more manageable it will be to correct the malalignment. Treatment options include:
- Orthodontic Braces: One of the most common and effective treatments for crossbites is through traditional braces. The braces function to gradually move the teeth into their correct position with the help of brackets and wires. For severe cases, other appliances may sometimes be added to help adjust the bite, such as rubber bands.
- Clear Aligners: For mild to moderate crossbites, clear aligners, like Invisalign, provide a less visible alternative to traditional braces. These custom-made removable trays gently aid in moving the teeth into alignment over time. Particularly favored by adults, aligners provide an alternative option that is less noticeable than traditional treatment.
- Palatal Expanders: Palatal expanders are commonly used in children whose jawbones are still developing. This device is placed in the upper jaw and gradually widened to correct a crossbite. Expanders help ensure that the upper teeth align properly with the lower teeth as they grow.
- Dental Restorations: Dental restorations which may involve the crowning or bonding of the teeth to improve their shape and alignment are mostly done in such cases. This option relates to minor crossbite.
- Tooth Extraction: When it comes to misaligned teeth or; in the case of overcrowding, one or more teeth can be removed in some instances to create space for proper alignment. This is usually used in combination with orthodontic treatment for the best results.
- Surgical Correction: Orthognathic surgery may be necessary when severe crossbites involve major jaw misalignment. This procedure repositions the jaw to improve alignment and function. In most cases, surgery is performed in adulthood, as jaw bones in children are still developing and may be correctable by non-surgical means.
Preventing Crossbite
While certain causes of crossbites, such as genetics, are not subject to prevention, there are effective steps parents and individuals can undertake to ensure that the chances of developing this condition are minimal.
- Stop toddlers between 2.5-3 years of age from thumb sucking and pacifier overuse.
- Have the child visit an orthodontist for regular check-ups to detect the early signs of misalignment.
- Seek early orthodontic evaluation, at least by age 7, to treat crossbites before they become worse.
- Promote nasal breathing rather than mouth breathing to encourage proper jaw development.
Conclusion
Crossbite is a simple dental condition which, if untreated, could lead to a whole lot of troubles with oral health, pain, and beauty. Fortunately, with diagnosis and treatment within the right time frame, crossbites are treatable so that a person in question might enjoy a healthier aligned smile. If you or your child has had crossbite signs, make sure you consult a dentist or orthodontist so as to establish the best course of treatment to avoid future complications.
Contact Us to Treat Your Crossbite
If you or your child exhibit signs of a crossbite, don’t hesitate to contact our dental office. We’re here to help correct the misalignment and relieve any discomfort, ensuring a healthier smile.





 |
|